end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
ETCO2 values during CPR do correlate with the likelihood of ROSC and survival and therefore have prognostic value. Cardiac arrest causes cerebral vasoconstriction that may impair tissue oxygenation brain perfusion and compromise neurological recovery.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
The use of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 measurement to guide management of cardiac arrest.

. Cardiac 255 and 18 mmHg pulmonary 337 and 17 mmHg pulmonary embolus 16 and 67 mmHg and unknown cause 205 and 97 mmHg30. Outcomes23 During cardiac arrest CPR functions to deliver substrate to vital organs. NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC.
End tidal normally 2-5 mmHg lower than arterial Comparing Arterial and End-tidal CO2 Review of Airway Confirmation Visualization Auscultation. Given the many potential confounders that can influence initial ETCO2 levels extreme or. PetCO2 partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide.
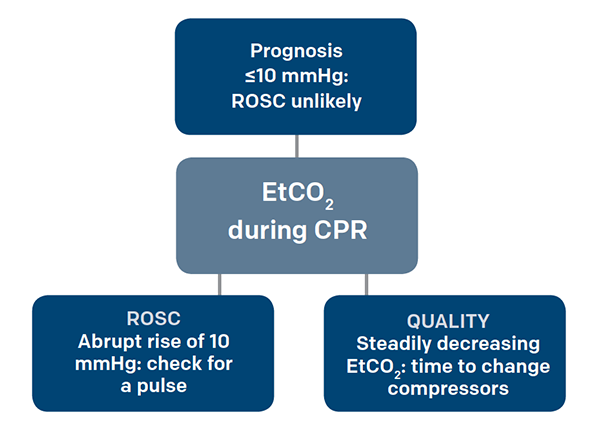
After 20 minutes of CPR death occurs if ETCO2 is consistently below 10 mmHg with 100 sensitivity and specificity 15. End-tidal carbon dioxide and els may have been underestimated3435 outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Normal range No measure of cardiac performance 1.
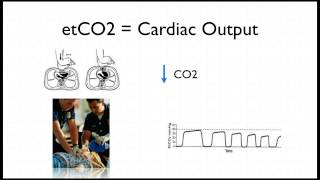
Measurement of end-tidal expiratory pressure of carbon dioxide ETCO 2 using capnography provides a noninvasive estimate of cardiac output and organ perfusion during cardiac arrest and can therefore be used to monitor the quality of CPR and predict return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. Variable because depends on the cardiac resuscitation manoeuvers lasting usually not more than 45 minutes NPi meaning has been described previously ETCO2 represents the amount of CO2 exhaled during ventilation in course of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The respective PETCO2values with ROSC versus no ROSC depending on the cause of cardiac arrest were as follows.
ETCO2 is a reliable indicator with a high prognostic value in determining the CPR outcome 11 12. When a capnometer is available and the machine is warmed-up connection to the ventilatory circuit takes. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
After 20 minutes of advanced cardiac life support ETCO2 averaged 39 - 28 mm Hg range 0 to 12 mm Hg in patients in whom the theoretical decision was made to cease field resuscitation. ROSC and neurologically intact survival after cardiac arrest. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa.
Scott Weingart describes titrating epinephrine in cardiac arrest to hemodynamic parameters and end tidal CO2. Correlation of NPi and end tidal CO2 ETCO2 and ROSC prediction Time Frame. Although certain ETCO2 cut-off values appears to be a strong predictor of mortality the utility of ETCO2 cut-off values during CPR to accurately predict the outcome of resuscitation is.
Studies have shown that in patients who had ETCO2 of 10 mmHg or less cardiac arrest was associated with death 13 14. MEASURING END-TIDAL CO 2 LEVELS DURING CARDIAC ARREST Presentation for MSBI Nurses Prepared by Dr. A sudden increase in ETCO2 is often the first sign of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC even before a carotid pulse can be detected.
Using an ETCO2 of 10 mm Hg or less as a theoretical. Quantitative relationship between end-tidal carbon dioxide and CPR quality during both in-hospital and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest Resuscitation. An end-tidal carbon dioxide level of 10 mm Hg or less measured 20 minutes after the initiation of advanced cardiac life support accurately predicts death in.
2Relate End-Tidal CO2 to ventilation perfusion and metabolism. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 monitoring is readily available easily used and a standard of care in the operating suite and in the critical care setting. Misting increased SaO2 Types of End-Tidal CO2 Qualitative Yes or No.
BackgroundPhysiology 2 Monitoring end-tidal CO. In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. It can be challenging to make the clinical decision when to terminate resuscitative efforts when caring for a.
Noninvasive measurement of ETCO2 has been shown to correlate with coronary perfusion pressure and myocardial perfusion during CPR Sanders et al. Negative Epigastric sounds Equal lung sounds Esophageal detector End tidal CO2 detector Secondary signs. CONCLUSIONS Based upon existing evidence ETCO2 levels do seem to provide limited prognostic information for patients who have experienced cardiac arrest.
End-tidal CO2 may be useful here as an easily and immediately measurable index of changes in cardiac output. Timing of defibrillation during cardiac arrest and CPR. Physiology and science behind End-Tidal CO2.
Indicator of impending ROSC 2. A ETCO2. Some distance away from the patient.
While end tidal CO2 is an excellent marker for chest compression quality and determining. Initial ETCO2 or 20-min ETCO220mmHg appears to be a better predictor of ROSC than the 10mmHg cut off value. Asphyxial cardiac arrest black bar primary cardiac arrest dotted bar.
In contrast survivors ETCO2 just before restoration of circulation averaged 31 - 53 mm Hg range 16 to 35 mm Hg P 0001. In contrast with AMSA end tidal CO2 ETCO2 mea-surements are commonly made during CPR. End-tidal pCO2 during cardiopulmonary resuscitation in all patients included in study.
Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC. On average during CPR if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 16-19 Lminm2 can be generated which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg. Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to.
Thus the PetCO2 lev- 12. Pierre Kory Laura OBrien RN CNS. After 20 minutes of CPR an end-tidal CO2 level of 19 mm Hg or less is predictive of death as an outcome of the cardiac arrest11.
Based upon existing evidence ETCO2 levels do seem to provide limited prognostic information for patients who have experienced cardiac arrest. Animal studies have shown that end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 detected during CPR is primarily dependent on pulmonary blood flow and is therefore a potential surrogate marker of perfusion during CPR46 However there. Your decreased cardiac output patients who.
In clinical observational studies mean ETCO 2 levels in patients with ROSC are higher. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle. An increase in etCO2 by 5 appears to have reasonable sensitivity 71-91 and specificity 94-100 for fluid responsiveness in two studies of patients breathing passively on the ventilator.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Pv Card Continuous End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In Cardiac Arrest Cardiac Nursing Cardiac Arrest Medical Knowledge

End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

Pv Card Continuous End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In Cardiac Arrest

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

End Tidal Capnography Can Be Useful For Detecting Diabetic Ketoacidosis Monitoring Copd Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Use Capnography For A Patient In Cardiac Arrest Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
